即使你是天才,如果你不努力,你也会被其它人超越。

扯淡
扯了那么多篇SpringBoot的相关案例,基本每行代码都是博主纯手工编写,附代码案例,懂Maven和Git的小伙伴必须可以手到擒来。
SpringBoot使得开发变的更加简洁,快速,当然被封装的越来越深。此时你就要引入越来越多的第三方工具类,虽然你可以把搭建好的项目运行起来,却无法理解是怎么跑起来的。有些人带着疑惑查阅文档,阅读源码,多年以后便成了大牛;有些人不求甚解,能跑就行,就这样干了N年CURD。
俗话说的好,燕雀安知鸿鹄之志哉?然子非鱼又焉知鱼之乐?curd并快乐着。每个人,都会有自己的成长轨迹,或平凡或精彩或或或或,快使用双节棍,嘿嘿哈嘿。
简介
好了,淡就扯这么多,今天与大家分享一款"超薄"的数据访问层框架Spring-data-jpa,依赖Hibernate,对Hibernate有一定的基础,可以更好的理解。
什么是spring-data
为了简化程序与数据库交互的代码,spring提供了一个现成的dao层框架,spring家族提供的spring-data适用于关系型数据库和nosql数据库。比如之前我们讲解的案例:
SpringBoot开发案例之整合mongoDB,当然还有Spring Data Solr,Spring Data Redis以及我们今天要分享的Spring Data JPA。
详解的可以参考:官网
什么是jpa
JPA全称为Java持久性API(Java Persistence API),JPA是java EE 5标准之一,是一个ORM规范,由厂商来实现该规范,目前有hibernate、OpenJPA、TopLink、EclipseJPA等实现。
如何使用JPA
查询
- 查询所有数据 findAll()
- 分页查询 findAll(new PageRequest(0, 2))
- 根据id查询 findOne()
- 根据实体类属性查询: findByProperty (type Property); 例如:findByAge(int age);
- 排序: findAll(sort )
- Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "age").and (new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "id"));
- 条件查询 and/or/findByAgeLessThan/LessThanEqual 等,
- 例如: findByUsernameAndPassword(String username , String password)
- 总数 查询 count() 或者 根据某个属性的值查询总数countByAge(int age);
- 是否存在某个id exists()
修改,删除,新增
- 新增:直接使用 save(T) 方法
- 删除: delete() 或者 deleteByProperty 例如:deleteByAge(int age) ;
- 更新:
@Modifying
@Query("update Customer u set u.age = ?1 where u.id = ?2")
int update(int age1 , long id);
项目结构
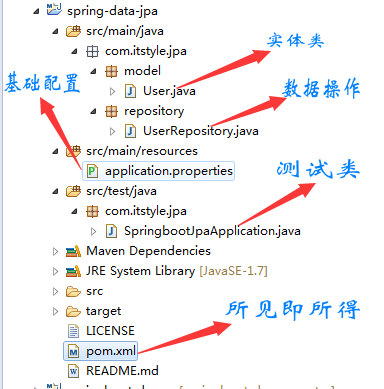
相关配置
pom.xml(部分代码,详见源码):
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>application.properties:
# 项目contextPath
server.context-path=/jpa
# 服务端口
server.port=8080
# session最大超时时间(分钟),默认为30
server.session-timeout=60
# 该服务绑定IP地址,启动服务器时如本机不是该IP地址则抛出异常启动失败,只有特殊需求的情况下才配置
#server.address=192.168.1.66
# tomcat最大线程数,默认为200
server.tomcat.max-threads=100
# tomcat的URI编码
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8
#注意中文乱码
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# Specify the DBMS
spring.jpa.database = MYSQL
# Show or not log for each sql query
spring.jpa.show-sql = true
# DDL mode. This is actually a shortcut for the "hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" property. Default to "create-drop" when using an embedded database, "none" otherwise.
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
# Hibernate 4 naming strategy fully qualified name. Not supported with Hibernate 5.
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming.strategy = org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
# stripped before adding them to the entity manager)
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialectspring.jpa.properties.hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto是hibernate的配置属性,其主要作用是:自动创建、更新、验证数据库表结构。该参数的几种配置如下:
- create:每次加载hibernate时都会删除上一次的生成的表,然后根据你的model类再重新来生成新表,哪怕两次没有任何改变也要这样执行,这就是导致数据库表数据丢失的一个重要原因。
- create-drop:每次加载hibernate时根据model类生成表,但是sessionFactory一关闭,表就自动删除。
- update:最常用的属性,第一次加载hibernate时根据model类会自动建立起表的结构(前提是先建立好数据库),以后加载hibernate时根据model类自动更新表结构,即使表结构改变了但表中的行仍然存在不会删除以前的行。要注意的是当部署到服务器后,表结构是不会被马上建立起来的,是要等应用第一次运行起来后才会。
- validate:每次加载hibernate时,验证创建数据库表结构,只会和数据库中的表进行比较,不会创建新表,但是会插入新值。
实体类 User.java:
package com.itstyle.jpa.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.*;
/**
* 用户实体(此处注意引用的注解包为javax.persistence*下面的)
* 创建者 科帮网
* 创建时间 2017年7月25日
*
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "sys_user")
public class User implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name = "id", nullable = false)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false, name = "age")
private Integer age;
--- 省略 get set 方法
}数据操作UserRepository.java:
/**
* 数据操作层
* 创建者 科帮网
* 创建时间 2017年7月25日
*
*/
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findByName(String name);
User findByAge(Integer age);
User findByNameAndAge(String name, Integer age);
List<User> findByNameLike(String name);
@Query("from User u where u.name=:name")
User findUser(@Param("name") String name);
}
小伙伴没有没有发现,我们只是定义了一个方法而已,怎么就这么奇妙的实现的对应功能?其实这是Spring-data-jpa的新特性,通过解析方法名创建查询。更多解析说明如下:
And => 等价于 SQL 中的 and 关键字 例如:findByUsernameAndPassword(String user, Striang pwd);
Or => 等价于 SQL 中的 or 关键字,例如:findByUsernameOrAddress(String user, String addr);
Between => 等价于 SQL 中的 between 关键字,例如:SalaryBetween(int max, int min);
LessThan => 等价于 SQL 中的 "<",例如: findBySalaryLessThan(int max);
GreaterThan => 等价于 SQL 中的">",例如: findBySalaryGreaterThan(int min);
IsNull => 等价于 SQL 中的 "is null",例如: findByUsernameIsNull();
IsNotNull => 等价于 SQL 中的 "is not null",例如: findByUsernameIsNotNull();
NotNull=> 与 IsNotNull 等价;
Like => 等价于 SQL 中的 "like",例如: findByUsernameLike(String user);
NotLike => 等价于 SQL 中的 "not like",例如: findByUsernameNotLike(String user);
OrderBy => 等价于 SQL 中的 "order by",例如: findByUsernameOrderBySalaryAsc(String user);
Not => 等价于 SQL 中的 "! =",例如: findByUsernameNot(String user);
In => 等价于 SQL 中的 "in",例如: findByUsernameIn(Collection<String> userList) ,方法的参数可以是 Collection 类型,也可以是数组或者不定长参数;
NotIn => 等价于 SQL 中的 "not in",例如: findByUsernameNotIn(Collection<String> userList) ,方法的参数可以是 Collection 类型,也可以是数组或者不定长参数;
创建一个按单字段排序的Sort对象: new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "description").and(new Sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "id"))
最终测试类SpringbootJpaApplication.java:
package com.itstyle.jpa;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import com.itstyle.jpa.model.User;
import com.itstyle.jpa.repository.UserRepository;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootJpaApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootJpaApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
try {
User user = new User();
user.setName("张三");
user.setAge(20);
userRepository.save(user);
List<User> u = userRepository.findByNameLike("%张三%");
System.out.println(u.size());
User us = userRepository.findByAge(20);
System.out.println(us.getAge());
us = userRepository.findByName("这是你干");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}偶遇问题
No identifier specified for entity:
检查一下包是否引入正确,引入一下:
import javax.persistence.*;中文乱码问题:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf-8在高版本mysql中需要指定是否进行SSL连接
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false代码:https://git.oschina.net/52itstyle/spring-data-jpa

